In today's world, maintaining a sterile environment is of paramount importance across various fields, from scientific research and mycology to electronics assembly and pharmaceutical compounding. A laminar flow hood, also known as a clean bench, plays a pivotal role in ensuring a contamination-free workspace.
However, the cost of purchasing a commercial laminar flow hood can be prohibitive for many individuals and small-scale operations. Fortunately, building your own DIY laminar flow hood is not only a cost-effective alternative but also a rewarding project that allows you to customize the hood to your specific needs.
In this extensive guide, we will delve deep into the process of constructing your own DIY laminar flow hood. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what a laminar flow hood is, why it is essential, and detailed step-by-step instructions on how to build one yourself. Let's embark on this journey to create a functional and budget-friendly sterile environment.
Understanding Laminar Flow Hoods
What is a Laminar Flow Hood?
A Laminar Flow Hood, often referred to as a laminar flow cabinet or clean bench, is a sophisticated piece of equipment used in various industries and laboratories, including microbiology, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and more. To grasp the significance of constructing your own DIY laminar flow hood, it's important to delve deeper into its functionality and purpose.
At its core, a laminar flow hood establishes a highly controlled and sterile environment by utilizing the principle of laminar airflow. This principle ensures that air within the hood moves in an organized, unidirectional manner, typically from the top of the enclosure down to the work surface. This controlled airflow serves the crucial purpose of providing a clean and particle-free workspace, free from contaminants that could compromise sensitive processes or experiments.
Laminar flow hoods are meticulously designed to meet stringent cleanliness and safety standards. They come in various configurations, such as horizontal and vertical flow hoods, and can be equipped with HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) or ULPA (Ultra-Low Penetration Air) filters to trap and remove airborne particles, bacteria, and other microorganisms.
These hoods are used for a wide range of applications, including tissue culture work, sample preparation, electronics assembly, and pharmaceutical compounding, where maintaining a sterile environment is paramount.
Read also our post on DIY Solar Panels
Why Do You Need a Laminar Flow Hood?
Understanding the significance of a laminar flow hood goes beyond mere acknowledgment; it is a critical component in environments where maintaining sterility is an absolute requirement. To appreciate its broad utility, let's explore some key applications that underscore the indispensable nature of a laminar flow hood:
- Microbiological Research: In the realm of microbiology, a laminar flow hood is an indispensable tool for cultivating and handling microorganisms in a meticulously sterile environment. Whether it's growing bacteria for research or conducting experiments with delicate microorganisms, the laminar flow hood creates a barrier against contaminants, ensuring the integrity of the work.
- Tissue Culture: For researchers engaged in cell biology and tissue culture work, the laminar flow hood is a lifeline. It provides a controlled environment that is essential for maintaining cell cultures free from contamination. This is especially crucial in studies involving cell lines, primary cell cultures, and tissue engineering.
- Electronics Assembly: In the electronics industry, where the tiniest speck of dust or particle can disrupt delicate components and circuits, a laminar flow hood plays a pivotal role. It shields electronic components from airborne contaminants, ensuring clean assembly processes, reduced defects, and enhanced product reliability.
- Mycology: Mycologists, those who study fungi and spores, rely on laminar flow hoods to carry out their work safely. These hoods prevent the dispersion of fungal spores into the surrounding environment, minimizing the risk of contamination and safeguarding both researchers and the integrity of their studies.
- Pharmaceutical Compounding: In pharmaceutical settings, the preparation of sterile drugs is of paramount importance. Laminar flow hoods are essential for compounding pharmacies and pharmaceutical manufacturers to maintain the required level of sterility throughout the drug formulation and packaging processes. This ensures that patients receive safe and contamination-free medications.
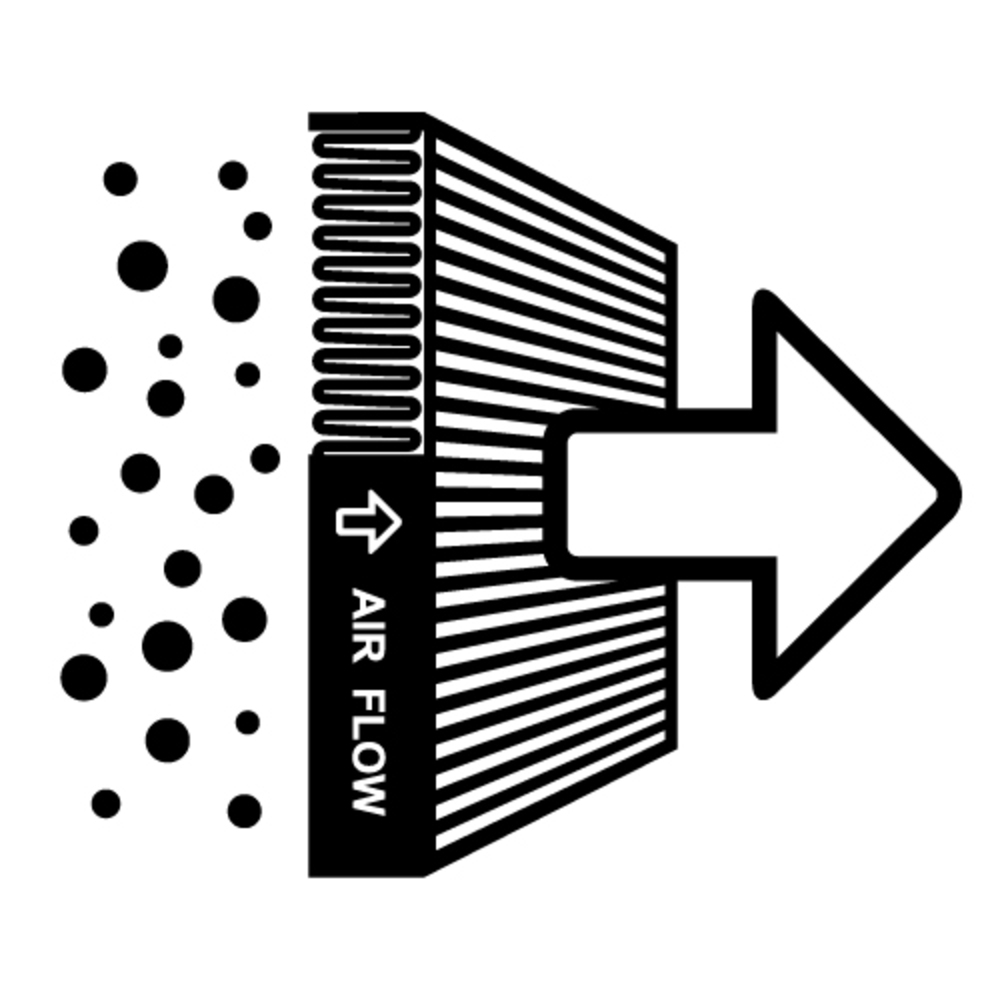
DIY Laminar Flow Hood Components
Before you embark on the construction journey, it's essential to gather all the necessary components. Let's take a closer look at each of these components, their functions, and considerations for selecting the right ones:
HEPA Filters
High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters are the heart and soul of any laminar flow hood. These filters are designed to remove particulates and microorganisms from the air, ensuring that the airflow remains consistently sterile. When selecting HEPA filters, it is crucial to choose ones with at least a 99.97% efficiency rating.
Fan/Blower
The fan or blower serves as the engine that generates the laminar airflow within the hood. It should have the capacity to push air through the HEPA filters and into the workspace at a consistent velocity. The choice of a fan or blower should align with the size and specifications of your laminar flow hood.
Work Surface
The work surface is the platform where you will conduct your sterile tasks. It should be crafted from a non-porous material that is both easy to clean and resistant to chemical corrosion. Popular choices include stainless steel and laminated particleboard. Ensuring that the work surface fits securely within the frame is crucial for maintaining a sterile environment.
Frame and Enclosure
The frame and enclosure of your DIY laminar flow hood provide the necessary structural support and help maintain the controlled environment. You have the flexibility to choose from a variety of materials for constructing the frame and enclosure, including plywood, acrylic, or metal. Proper sealing of the enclosure is essential to prevent any air leaks.
Lighting
Good visibility is paramount when working within the hood. Adequate lighting ensures that you can carry out your tasks with precision and accuracy. Opt for cool, white fluorescent or LED lights that emit minimal heat and provide uniform illumination across the work surface.
Read also our post on DIY Day
Construction Steps
Design and Planning
Before diving into the physical construction, meticulous planning is key. Design your DIY laminar flow hood, taking into consideration the dimensions, placement of filters and fan, and the precise location of the work surface. Your design should adhere to safety guidelines and ensure proper airflow within the hood.
Building the Frame
The frame of your laminar flow hood provides structural integrity and support for the entire setup. Construct it according to your pre-planned design, ensuring sturdiness and airtightness to prevent any unwanted air leaks. The front opening of the hood should have a transparent material that allows for visibility while working.
Installing the Fan and Filters
Proper installation of the fan and HEPA filters is critical for the effective operation of your laminar flow hood. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully, ensuring that the airflow direction remains unidirectional, moving from the top of the hood down towards the work surface. Seal any gaps meticulously to prevent air leaks that could compromise sterility.
Creating the Work Surface
With the frame and fan in place, it's time to install the work surface. The work surface should be securely positioned within the hood, with ample space for your tasks. Choose a material that is easy to clean and maintain, as well as resistant to chemical exposure.
Adding Lighting
Illumination is critical for precision and visibility while working within the laminar flow hood. Install the lighting system inside the hood, ensuring that the lights are strategically placed to eliminate shadows and provide uniform lighting across the work surface.

Safety Considerations
Safety considerations are paramount when building and operating a DIY laminar flow hood to ensure both the effectiveness of the system and the protection of personnel and processes. Here, we delve into these crucial safety considerations in greater detail:
- Regular Testing and Calibration: It is imperative to routinely test and calibrate your laminar flow hood. This ensures that the hood consistently maintains the prescribed airflow velocity and sterility levels. Regular checks and adjustments, in accordance with manufacturer guidelines or established protocols, guarantee that the hood remains in optimal working condition. Failure to do so could compromise the sterility and effectiveness of the controlled environment.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): As a standard safety practice, always don appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working within or near the laminar flow hood. This includes wearing gloves, lab coats, and any other required protective gear. These precautions minimize the risk of introducing contaminants from personnel into the sterile workspace and help maintain the integrity of the controlled environment.
- Workspace Cleanliness: Maintaining a pristine work area within the laminar flow hood is of paramount importance. Preventing contamination from external sources is contingent on cleanliness and organization. Regularly clean and disinfect the interior surfaces of the hood and surrounding areas. Keep all necessary tools and materials neatly arranged to minimize the risk of accidental contamination during tasks.
- Minimize Disruptions: The primary purpose of a laminar flow hood is to provide a controlled, unidirectional airflow that safeguards the work area from contaminants. To maintain the integrity of this airflow, it is essential to minimize unnecessary movements and disruptions within the hood. Limit the opening and closing of the hood as much as possible and avoid activities that generate turbulence, as these can compromise sterility.
- Aseptic Techniques: Adherence to proper aseptic techniques and procedures is fundamental to prevent contamination during tasks conducted in the laminar flow hood. Familiarize yourself with established aseptic practices, such as handwashing, sterilization of equipment and materials, and sterile handling of samples and instruments. Consistently practicing these techniques ensures that the controlled environment remains uncontaminated.
Read also our post on DIY Test Light
Maintenance and Calibration
Maintaining the long-term functionality and reliability of your DIY laminar flow hood is essential to ensure consistent and dependable performance. To delve further into this topic, let's explore key aspects of maintenance and calibration that should be an integral part of your workflow:
- Filter Maintenance: HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are the heart of your laminar flow hood, responsible for trapping and removing contaminants from the air. It is imperative to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for filter maintenance. This includes regular cleaning or replacement of filters to ensure optimal filtration efficiency. Neglecting filter maintenance can lead to decreased airflow quality and a compromised sterile environment.
- Airflow Velocity Checks: Periodic measurement and verification of airflow velocity are essential to guarantee that your laminar flow hood operates within the required standards. This involves using an anemometer or airflow meter to measure the velocity of the air as it flows through the hood. Ensuring that the airflow velocity remains within the specified range is critical for maintaining a controlled and sterile workspace.
- Component Inspection: Routinely inspect all components and elements of the laminar flow hood for signs of wear and tear. This includes scrutinizing the integrity of the hood's structure, the condition of the working surface, and the functionality of the control panel. Any damaged or deteriorating components should be promptly identified and replaced to prevent operational issues and maintain the safety and sterility of the hood.
- Calibration Verification: Beyond routine maintenance, verifying the accuracy and precision of your laminar flow hood is essential. Calibration checks are used to ensure that the hood operates within specified parameters. This entails comparing the actual performance of the hood to established standards and correcting any deviations that may occur over time. Regular calibration helps maintain the reliability and consistency of the laminar airflow and sterility levels within the hood.

FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is a laminar flow hood, and why do I need one?
A laminar flow hood is a controlled environment that uses laminar airflow to maintain sterility. It is essential for tasks that require aseptic conditions, such as microbiological research, tissue culture, and electronics assembly. It creates a workspace where airborne contaminants are minimized, ensuring the integrity of your work to build a laminar.
How much does it cost to build a DIY laminar flow hood?
The cost of building a DIY laminar flow hood can vary depending on the size and quality of components you choose. Generally, you can expect to spend anywhere from $500 to $2,000 for materials and components. This is significantly cheaper than purchasing a commercial laminar flow hood, which can cost several thousand dollars build a laminar flow hood.
What are the essential components of a DIY laminar flow hood?
The key components include HEPA filters, a fan or blower, a work surface, a frame and enclosure, and lighting. HEPA filters ensure the air is sterile, while the fan creates laminar airflow. The work surface is where you perform tasks, and the frame and enclosure maintain the controlled environment. Lighting provides visibility.
Do I need special skills or tools to build a DIY laminar flow hood?
While building a laminar flow hood is a relatively advanced DIY project, it doesn't require specialized skills. Basic woodworking and assembly skills, along with common hand and power tools, are sufficient. Attention to detail and safety precautions are essential laminar flow hood for mushroom.
Where can I find the necessary components for my DIY laminar flow hood?
Components such as HEPA filters, fans, and lighting can be sourced from reputable suppliers, including laboratory equipment suppliers and HVAC suppliers. You can also find some components online through retailers and specialty stores.
What are the safety considerations when using a DIY laminar flow hood?
Safety is paramount when working with a laminar flow hood. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and lab coats. Keep the workspace clean and organized, minimize disruptions, and follow aseptic techniques to prevent contamination.
How do I maintain and calibrate my DIY laminar flow hood?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning or replacing HEPA filters, inspecting components for wear and tear, and verifying airflow velocity. Calibration checks should ensure that the laminar flow hood operates within specified parameters. Refer to the manufacturer's guidelines for specific maintenance intervals and procedures.
Can I modify the DIY laminar flow hood design to fit my specific needs?
Yes, one of the advantages of building your laminar flow hood is the flexibility to customize it to your requirements. You can adjust the size, configuration, and features to suit your specific applications while adhering to the principles of laminar airflow.
Is building a DIY laminar flow hood worth the effort?
Building a DIY laminar flow hood can be a cost-effective and rewarding endeavor, especially if you require a sterile workspace for your projects or research. It allows you to have a customized solution that meets your needs without the high cost of commercial alternatives.
Are there any legal or regulatory requirements for using a DIY laminar flow hood?
Depending on your location and the specific applications, there may be regulatory requirements or guidelines related to the use of laminar flow hoods in certain industries. It's essential to research and comply with any relevant regulations or standards applicable to your work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, building your own DIY laminar flow hood is an excellent solution for creating a sterile environment tailored to your specific needs while keeping costs manageable. The journey to constructing this critical piece of equipment may seem daunting, but with a clear understanding of the principles of laminar airflow and the step-by-step instructions provided in this guide, you are well-equipped to embark on this project.
Remember that safety and ongoing maintenance are key to the long-term success of your DIY laminar flow hood. By consistently implementing proper practices, you can enjoy the benefits of a sterile workspace without breaking the bank. Whether you are a researcher, mycology enthusiast, or someone with a need for sterile conditions, your DIY laminar flow hood can become an invaluable asset in your endeavors.
Sources
https://scholarworks.utep.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3793&context=open_etd
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10403924/
https://www.unh.edu/research/biosafety-cabinets-and-clean-benches




